Discover What the Eye Cannot See
Remote Sensing: Your Window to a New Perspective of the World
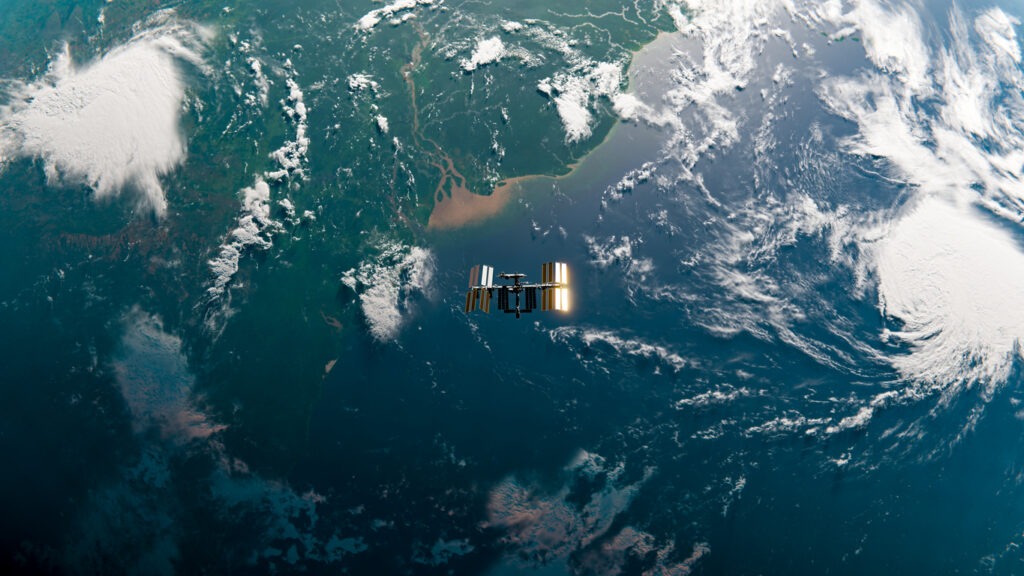

Earth and its components without direct contact. This is achieved through advanced technologies and devices, such as satellites and aircraft, which capture data and transform it into actionable insights useful for various sectors
The process of remote sensing involves key stages, from data acquisition to analysis and actionable insights:
Data Acquisition:
- The process begins with a source of energy, such as sunlight or artificial waves like radar.
- Energy interacts with the Earth’s surface, where some is absorbed, and some is reflected toward sensors mounted on aircraft or satellites.
- The collected data is transmitted to ground stations, where it is converted into digital images or data.
Data Analysis:
- Advanced tools analyze the received images.
- Data is combined with other information using systems like GIS to provide comprehensive and accurate insights.
The Evolution of Remote Sensing Over Time
Remote sensing has undergone significant advancements over the decades, driven by technological progress:
- 1900: Balloons, kites, and pigeons were used for aerial photography.
- 1909: The first aerial photo was taken using an airplane in Italy.
- 1957: The Soviet Union launched the first satellite, “Sputnik 1,” marking the start of space-based remote sensing.
- 1961: Yuri Gagarin’s first human spaceflight opened new horizons for space sensing.
- 1972: The U.S. launched “Landsat 1,” revolutionizing Earth observation.
- 1986: The French satellite “Spot” provided higher-resolution imagery.
- 1999: The U.S. launched “Ikonos,” offering high-resolution images with a spatial accuracy of 0.5 meters.
This continuous evolution has enabled more precise and comprehensive understanding of the environment, natural disasters, and infrastructure.
- Damage Assessment: Evaluating the impacts of disasters such as floods and earthquakes.
- Resource Management: Monitoring environmental changes like desertification and forest coverage.
- Urban Planning: Supporting sustainable city and infrastructure development.
- Agricultural Applications: Monitoring crop health and improving productivity.
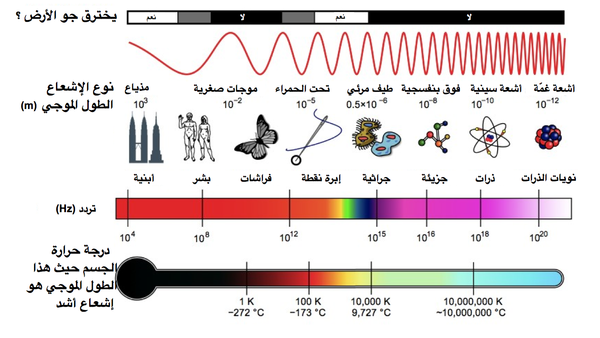
Remote sensing technologies rely on the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes various types of waves, some visible to the human eye and others invisible:
- Visible Light: Used to produce color images that highlight details such as terrain and vegetation.
- Infrared Waves: Detect thermal differences in objects, helping monitor plant health and groundwater levels.
- Microwaves and Radar: Useful for terrain mapping in all weather conditions, penetrating clouds and dust.
- Gamma Rays: Used to detect geological formations and cracks in infrastructure.
Our Service
What We Offer
We provide innovative solutions utilizing remote sensing technologies to analyze data and deliver precise insights to support your projects. Whether you’re working in agriculture, urban planning, or resource management, our technologies help you maximize the potential of your data.
Contact us today to learn how we can support you with remote sensing technologies to see the world in new and innovative ways


